Japanese Scientists Create the World’s Smallest Video Game Using Nanoparticles
|
|
Key points
- Japanese researchers created a game using electron beams to control nanoparticles in real time.
- The game allows players to control a spaceship-like object and shoot at nano-sized polystyrene balls.
- Beyond gaming, the technology could have major applications in nanotechnology, 3D printing, and targeted drug delivery.
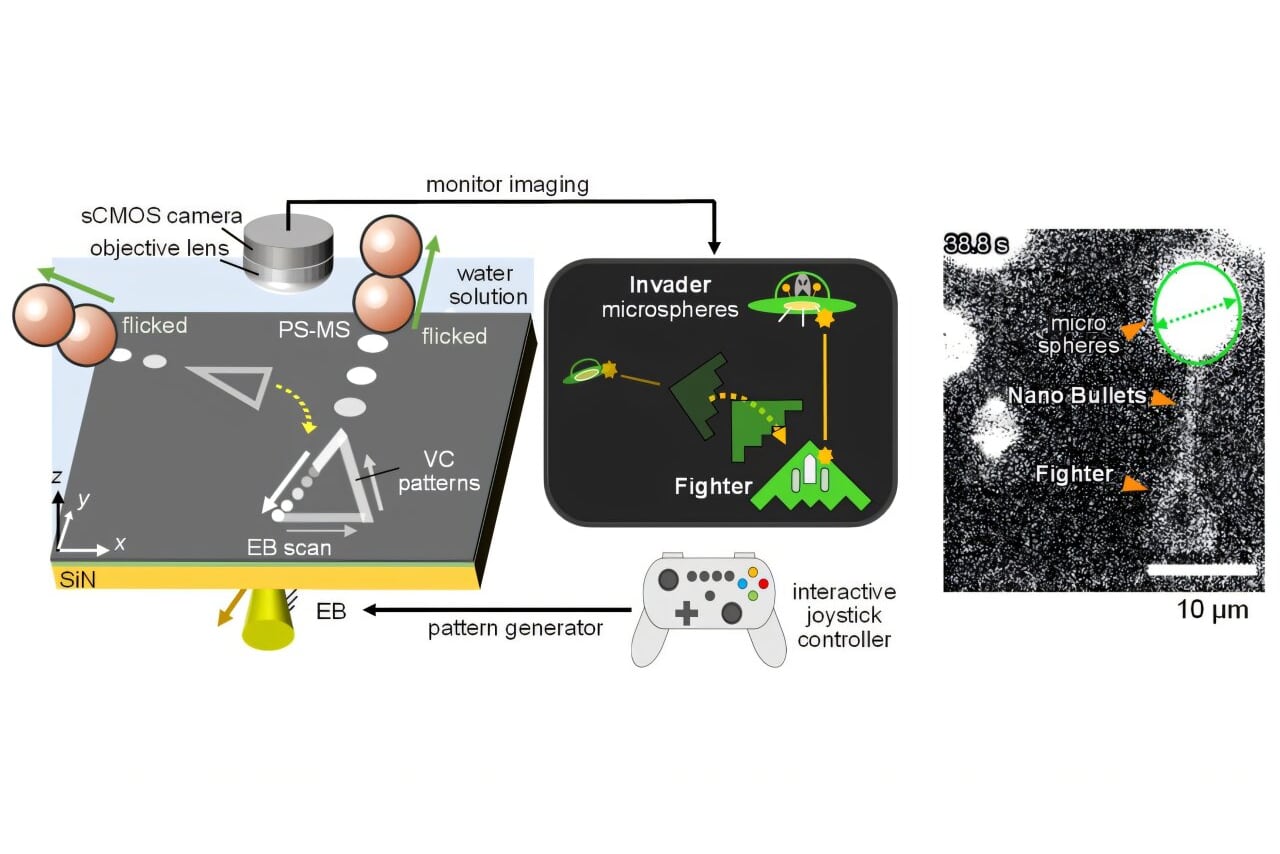
A research team led by Professor Takayuki Hoshino of Nagoya University’s Graduate School of Engineering has developed what they call the world’s smallest shooting game, manipulating nanoparticles approximately one billionth of a meter in size in real time. The study, published in the Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, is a step toward creating nano-mixed reality (MR)—a technology that merges virtual environments with physical nanomaterials.
The game uses high-speed electron beams to generate electric fields and optical images, allowing researchers to control nanoparticles in real time. Inspired by classic arcade shooters, the team designed an interactive game where players maneuver a spaceship-like object to shoot at nano-sized polystyrene balls. A gamepad controls the electron beam, adjusting the force field acting on the particles, blending digital and physical elements seamlessly.
“The system projects the game ship onto real nanophysical space as an optical image and force field, creating an MR where nanoparticles and digital elements interact,” Hoshino explained. “The player manipulates a ship and shoots bullets at real nanoparticles to repel them, demonstrating real-time interaction between digital data and physical nano-objects.”
Beyond gaming, this breakthrough has major implications for nanotechnology and biomedical engineering. The ability to manipulate nanoparticles with such precision could revolutionize fields like 3D printing, material science, and targeted drug delivery. “We could 3D print nano-objects in real time, fundamentally changing the way materials are built at the smallest scales,” Hoshino said. “This same technique could also be used to guide toxic agents to virus cells in living organisms, offering a new approach for treating diseases.”














